Series
Corpus - au coeur des organes
29 episodes
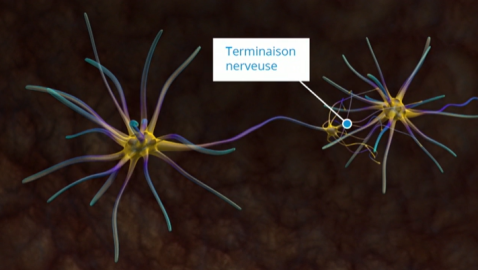
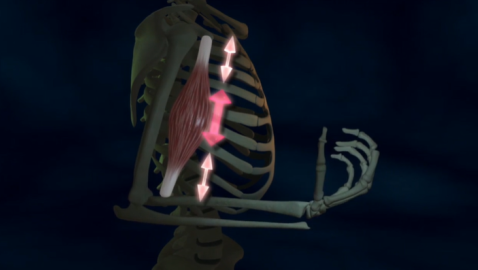
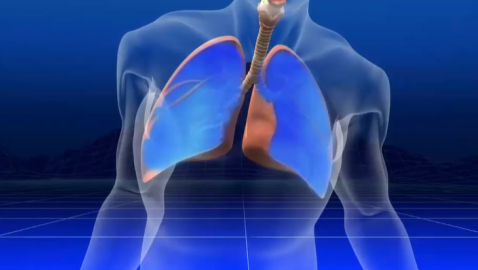
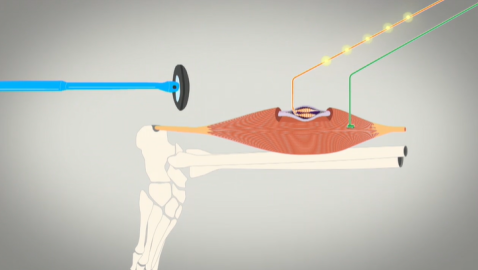
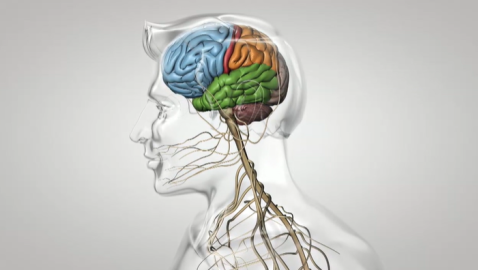
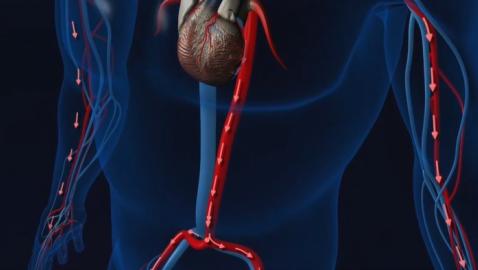
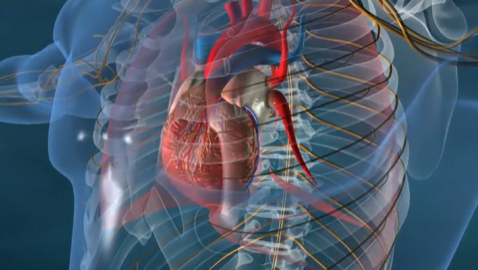
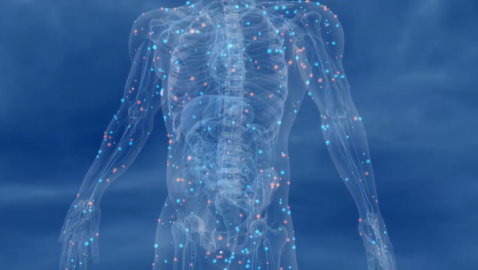
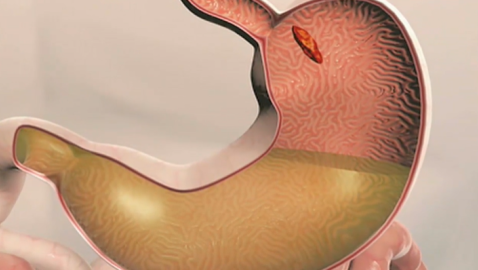
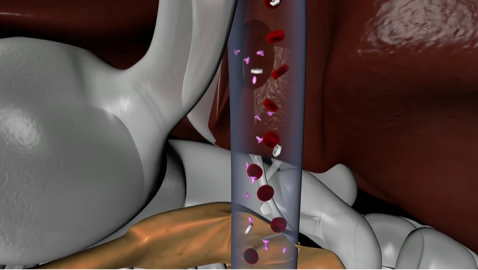
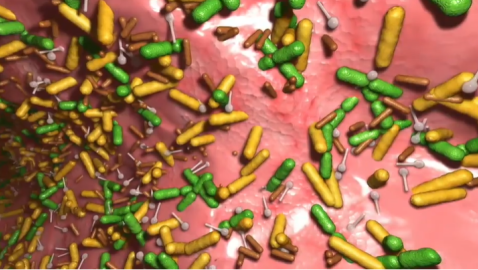
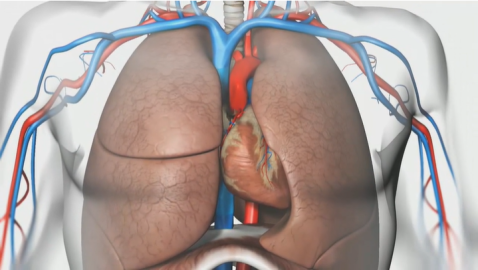
This informative series provides a better understanding of organ function and systemic organization. The series combines real medical images with animated graphics, to give a better understanding of the complexity of the human body.
Watch
Share